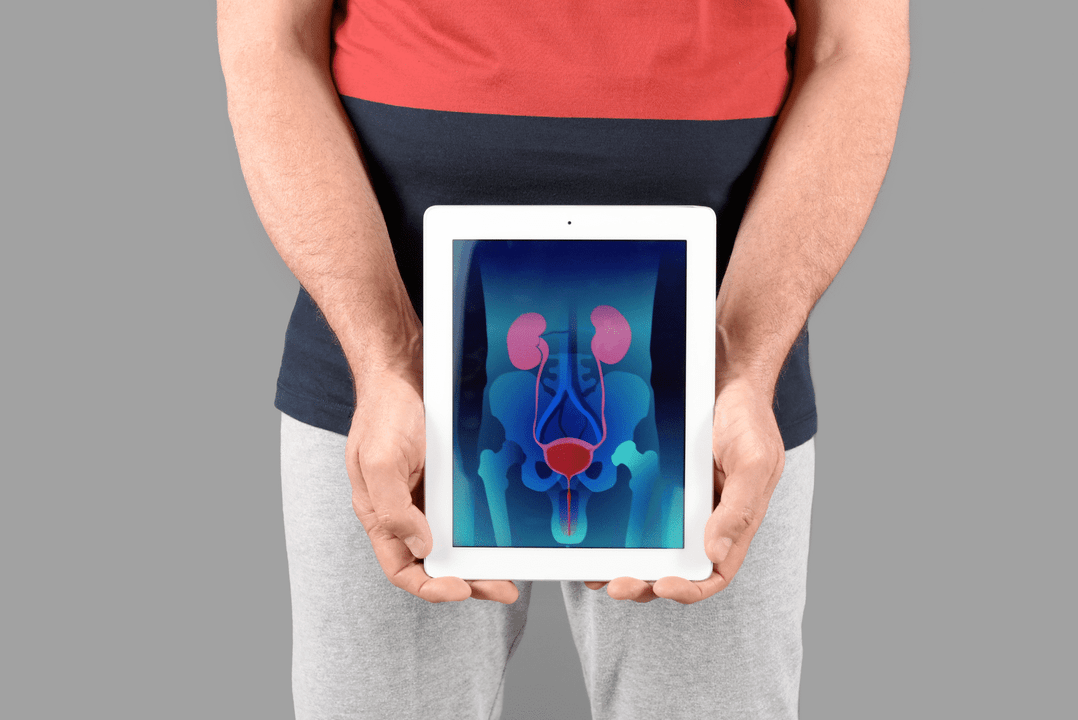
What is prostatitis? This is an inflammatory disease of the prostate gland. Only men have a prostate gland, so this disease at first glance is only relevant for them, but in fact it also affects the lives of ordinary sexual partners.
Cause of disease
What causes prostatitis? There is a myth that prostatitis can occur either from bacteria or from hypothermia. In reality, the situation is a little different. There are often bacteria in the prostate gland, and hypothermia is just a predisposing factor that can trigger the onset of inflammation.
When hypothermia occurs, a violation of blood microcirculation occurs, which impairs the blood supply to the pelvic organs. As a result, the amount of blood around the prostate changes. There are fewer blood cells that fight bacteria, and they can no longer cope with the load. It turns out that hypothermia causes the development of the inflammatory process and is an indirect cause of the development of prostatitis.
Chronic and acute diseases
How does acute and chronic prostatitis manifest? Symptoms of prostatitis in acute form make themselves felt by sharp pain, high fever, painful urination with weak pressure. With chronic prostatitis it is more difficult. The symptoms can be easily confused with simple lethargy, so the patient believes that nothing terrible happened: he sat somewhere cold, tired, or ate something.
The following manifestations of chronic prostatitis symptoms are known:
- aching pain in the perineum;
- whining pain radiating to scrotum;
- disturbing pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the sacrum, coccyx, and penis;
- impaired urination during prostatitis is characterized by weak or normal pressure, but sometimes these symptoms are not expressed;
- Some patients experience problems with erection, most often of a psychological nature, because the direct relationship between inflammation in the prostate and potential disorders has not been identified.
Preventive measures
How often should you have sex to avoid prostatitis? What is prostatitis prevention?
The prostate gland produces what is called prostatic secretion - a viscous liquid that contains components that are also found in sperm. The fluid part of the semen is the secretion of the prostate and the secretion of the seminal vesicles, which are located behind the prostate gland. At a young age, a man always has a morning erection, which is accompanied by the production of prostate secretions. If sexual intercourse does not take place, it accumulates day after day. This leads to stagnation, which then causes a slight increase in the size of the prostate and pain - a disturbing pain occurs in the perineum.
Nature means that every erection should end with ejaculation. I wake up 30 times in a month - 30 erections, which means 30 sexual intercourse! There is a generally accepted opinion in urology that an average of 22 ejaculations are needed to prevent prostatitis, but again this is only a recommendation. In practice, this is sometimes very difficult to achieve, and everyone has different needs for sex.
What tests should be taken?
What tests should be taken if you have or suspect prostatitis? First of all, this is a general blood test, as well as a general urine test.
During the consultation, the urologist performs a comprehensive examination, during which a digital rectal examination is performed. The doctor examines the prostate, palpates it, assesses pain, consistency, and elasticity. In this case, prostate secretions are collected for analysis.
Tests for prostatitis suggest:
- Evaluation of leukocyte count. The more, the more active the inflammatory process.
- Examination of prostate secretions for bacterial culture. Allows you to identify which bacteria cause inflammation, in what quantity they are present, and which drugs act against them, and which are completely useless.
- Take a smear for sexually transmitted infections.
- Transrectal ultrasound examination. This is the most informative procedure that allows you to get information about the state of the prostate, its structure and volume.
How long does it take to treat prostatitis?
It all depends on the type of prostatitis. For diseases caused by bacteria, antibiotics must be prescribed. Due to the peculiarity of the porous structure of the prostate and the specific blood supply to this organ, treatment with antibiotics and other drugs lasts for 28 days.
The blood supply to the prostate is located in the periphery, so for 20 days of taking antibiotics there is a cumulative effect, and only from days 20 to 28 the drug reaches the desired therapeutic concentration. That is why it is important to take the medicine for the duration recommended by the doctor.
Other medicines
In addition to antibiotics, they also prescribethe following drugs:
- Probiotics that restore intestinal microflora.
- Antifungal medication. When taking antibiotics, the activity of the immune system decreases, and fungal diseases (most often candida albicans or thrush) begin to appear in men, even if they have only one sexual partner.
- Vitamins.
- Preparations to improve blood microcirculation.
- Antiplatelet agents that thin the blood. They are prescribed to ensure that the blood supplies the tissues well and carry the medicine prescribed to them.
Treatment is not medicine
- Prostate massage helps relieve congestion.
- First, the massage mechanically squeezes out the mucus and bacteria that accumulate in the prostate.
- Second, blood supply and lymphatic drainage are improved.
- Physiotherapy and hardware treatment. Vibrolaser magnetic therapy gives good results. Lasers increase the permeability of cell membranes for drugs, they penetrate the prostate, and under the influence of magnets, lymphatic drainage improves, which is enhanced by vibration therapy.
What will happen if not treated?
If prostatitis is not treated, then:
- The risk of male infertility increases. Prostate secretions are part of the sperm, so bacteria and all the bacterial wastes spoil the quality. Sperm become less active, and there is a struggle for nutrients (fructose, citric acid, zinc) between bacteria and sperm. As a result, the sperm becomes weak and loses its ability to fertilize.
- Various adhesive processes can form in the vas deferens. This leads to the fact that the sperm is not released and does not enter the egg.
- Frequent nagging pains may appear. Sometimes some patients are lucky, and for some time nothing bothers them, and they think that the disease has receded by itself. But then the symptoms return and get worse.
"Do's" and "don'ts" for prostatitis
What can you eat?
- Salty can be, but without abuse (add a little salt to food).
- Alcohol – maybe in minimal quantities (a glass of wine or 50 g of cognac, whiskey every night).
- Coffee - 1-2 cups a day is allowed, in large quantities it is prohibited, because coffee leads to vasoconstriction and worsening blood microcirculation.
Is it possible to have sex?
If the ejaculation itself does not cause sharp painful sensations, then it is possible, even necessary, to live a sexual life. If sexual intercourse causes pain or discomfort, it is better to refrain from sexual activity during the treatment period.
Is it possible to visit the bath, sauna, hammam?
Here everything depends on the degree of prostatitis. If this is an acute process with fever, then there is no need to visit those places. If the treatment for prostatitis goes as usual and there are no alarming symptoms, visiting the bathhouse or swimming pool in doses is not prohibited. But you need to reduce your stay in the steam room, as well as in cold water, to a minimum.
Is physical activity necessary?
It is impossible to do without physical activity at all; physical exercise that can be performed is the best helper in the treatment of prostatitis. The main thing is not to expose the body to increased stress from training. You can walk, run, squat, etc.
As for bicycles, not everything is clear. Doctors do not recommend this sport for men (except only in the form of a short walk). When a man sits on a bicycle, the blood vessels in the pelvis and perineum are pressed and the blood supply is disrupted. There is no direct connection, but when it comes to prevention, we try to exclude all possible factors, even if they are not directly influencing.
Do I need to treat my sexual partner?
Treatment is required for the partner only if a sexually transmitted infection is detected. In fact, prostatitis is not transmitted through sexual contact, so treatment is usually not necessary for couples, although examination by a gynecologist will not hurt.